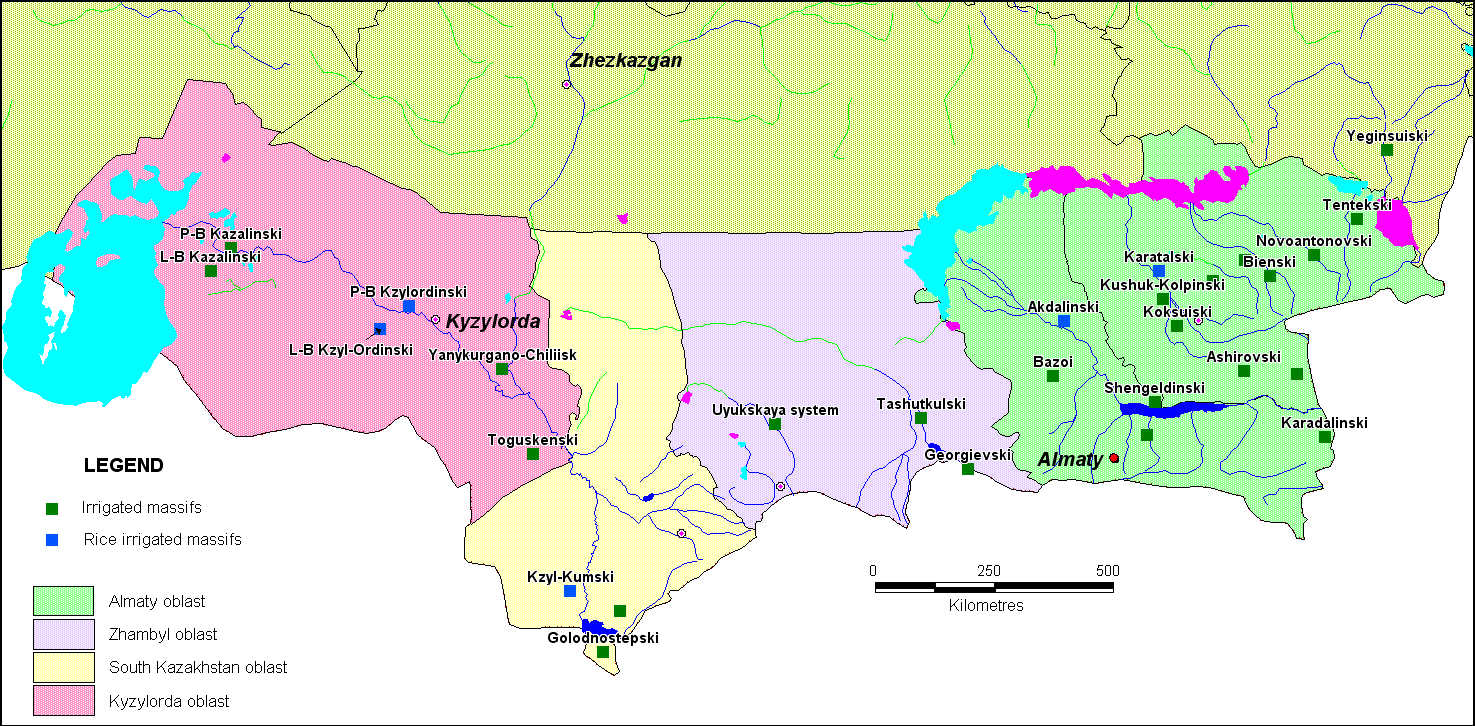

Schematic positioning of irrigated regions of southern part of Kazakhstan
Water resources deficiency, especially in southern regions, begun to appear more sharply during last years in connection with annual decrease of trans-boundary rivers discharges volume and with water consumption increase by industrial branches of economics at adjoining states. Water deficiency is already characteristic for the basins of Aral, Balkhash, Ural, flowless river basins of Shu, Sarysu, Talas, Turgai, Nura.
The maximal volume from all users of river water on the south of Kazakhstan is expended to irrigating agriculture. About 1400 thousands of hectars of irrigating soils is used in Kazakhstan during recent years. (Round table. Improvement of legislation as of irrigating agriculture problems and the ways of effective use of irrigating soils in Kazakhstan, 19.05.2010). 93% of them are situated in four southern regions of the Republic: Almatinskaya, Zhambylskaya, Yuzhno-Kazakhstanskaya, Kyzylordinskaya. These regions are situated in arid zone, in conditions of insufficient watering, where it is necessary to make man-made irrigation for receiving of guaranteed harvest of agricultural products. Surface waters are irrigating source for the majority of irrigating systems. Water intake for agriculture in 2010 year was equal to more than 12 billions of cubic meters.
Such cultures as grain, feed, cotton, vegetable, corn, soybean, beet-sugar, and also cucurbit cultures are cultivated on irrigated soils. Irrigation of the majority of cultures is made by various methods: by flooding, by furrow, by sprinkling.
As the most moisture-holding culture is rice, which is cultivated on the Akdalinski and Karatalski areas of irrigation in Almatinskaya region, and also on irrigating areas of Kyzylordinskaya region. Kyzylordinskaya region is the centre of rice cultivation in Kazakhstan. In spite of the fact that at total volume of cultivated agricultural products, the part of rice is equal to 6%, for its production are expended large volumes of irrigating waters. Constant flooding of rice checks and flow regime of irrigation lead to ground waters level raise under irrigated areas and to the formation of large volumes of drainage-discharge waters. Actual use of water on irrigated soils considerably exceeds the scientifically substantiated norms because of unproductive water losses. It is noted on many irrigating systems the unsatisfactorily technical condition of water in taking systems, of irrigating and drainage channels; the greater part of channels are laid in soiled beds, in the result of which water volumes for filtration are increasing and irrigated soils are not provided with water.
 |
|
 |
|||||||||
Previous |
Next |