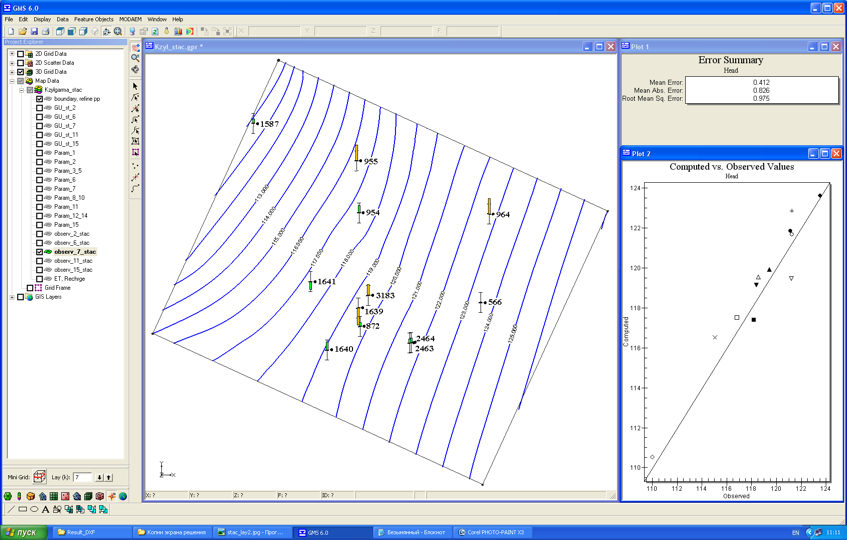
Model calibration included reverse stationary task solution, and also the calculation and analysis of balance components of groundwaters flow.
Reverse stationary solution
More precise definition of the prepared maps of water conductivity of permeable layers and filtration coefficients of dividing them weakly permeable layers has been the aim of the reverse stationary task solution. During solution of the reverse stationary task on the model, hydrogeological conditions existing at conditionally undisturbed period by state for the beginning of the year 1974, were reproduced.
As the initial were taken the values of water conductivity, received in the result of processing of experimental-filtrational works. The solution has been repeated up to satisfactorily coincidence of calculated and actual measured levels in wells. Coming from experience of modeling it has been taken the decision, that allowable mistake of the task solution concerning heads must not be above 10-15% from values demanded.
Inverse stationary task solution error for the Upper Turonian aquifer

| Schematic map of water conductivity of Maastrichtian aquifer
|
Schematic map of water conductivity of Coniacian-Campanian aquifer
|
| Schematic map of water conductivity of Upper Turonian aquifer
|
Schematic map of water conductivity of Upper Albian-Senomanian aquiferous complex
|
| Schematic map of water conductivity of Low-Middle Albian aquiferous complex
|
| Values of separating layers conductivity
Values of water conductivity collected from reverse stationary task solution results of Maastrichtian, Coniacian-Campanian, Upper-Turonian aquifers, Upper-Albian-Senomanian and Lower-Middle-Albian aquiferous complexes do not contradict with experimental data and results of experiments executed earlier. Minimal filtration coefficients (2*10-7 – 5*10-6 m/day) correspond with Coniacian-Campanian clayish deposits layer. Values of filtration coefficients for clayish deposits layer are higher. They are changing from 4*10-6 to 1*10-5 m/day. For layer of Lower-Middle-Albian clayish deposits filtration coefficient are in the limits of 5*10-6 to 2*10-5 m/day. Tendency of filtration coefficients increase for clayish deposits in the direction from north-west onto south-east is observed. Collected on the model values of filtration coefficients of dividing clayish layers do not contradict with experimental data and results of investigations executed earlier. It is possible to conclude that preciseness of reverse stationary task solution corresponds with demands imposed to the model of Kyzylzharminski groundwaters deposit. |
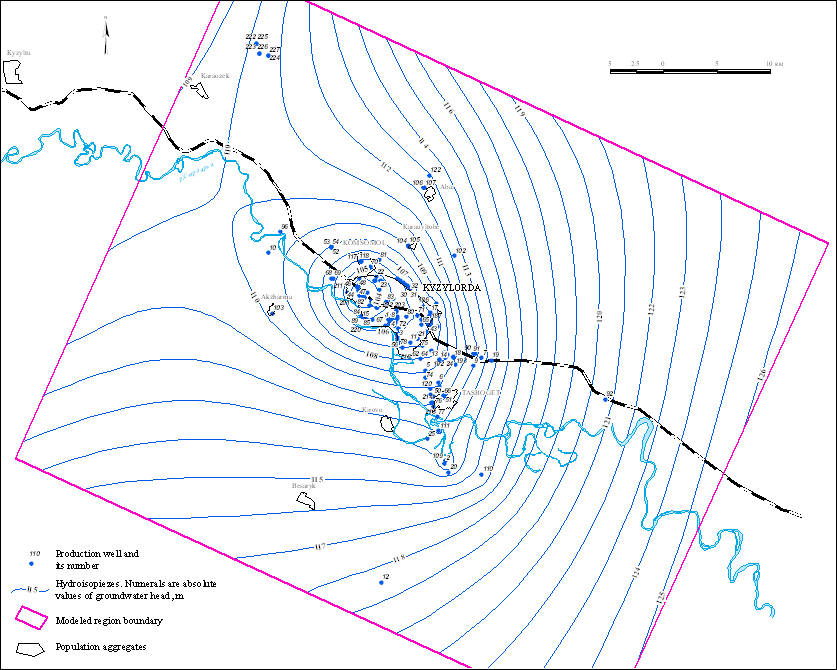
Map of hydroisopiezes of Upper Turonian aquifer as of the state for the year 1974.
|
Reverse non-stationary task solution
| As the aim of reverse non-stationary task solution was more exact determination of elastic water yield of water bearing rocks. During its solution on the model the change of hydrogeological conditions was reproduced from the year of 1974 (conditionally non-disturbed period) up to 1.10.2010. The step of solution of reverse non-stationary task is one year. Water take-off by production wells was executed from Coniacian-Campanian, Upper-Turonian and Upper-Albian-Senomanian aquifers.
Calculated on the model groundwaters levels were compared with actually measured ones by regime wells. Values of elastic water take-off coefficients of rocks were gathered. As the initial ones were adopted the values, produced in the result of processing of experimental-filtrational works. The solution was repeated up to the satisfactory coincidence of calculated and actually measured levels in wells. In accordance with experience of modeling it has been taken that allowable error of task solution concerning heads must not be over 10-15% from values demanded. Collected values of resilient water take-off coefficients of the rocks are: for Maastrichtian aquifer – 7*10-6 1/m, for Coniacian-Campanian aquifer – 1*10-5 1/m, for Upper-Turonian aquifer – 1*10-5 1/m, for Upper-Albian-Senomanian aquifers – 1 |
Map of hydroisopiezes of Upper Turonian aquifer as of the state for the October 2010
Calculated levels in whole satisfactorily coincide with the results of regime observations.
Collected on the model values of resilient water take-off of rocks do not contradict with the experimental data and with the results of investigations made earlier. At the process of solution of reverse non-stationary task on the model water take-off from 1974 to 2010 has been reproduce by actual data. The conclusion can be made that preciseness of reverse non-stationary task solution corresponds with the demands put to the model of Kyzylzharminski groundwaters deposit. The model adequately reflects the hydrogeological conditions existing on the undisturbed period (1974), their changes, having taken place in the result of groundwaters exploitation from 1974 up to 2010 and can be used for solution of prognostic hydrodynamic task. |
Integrated graphs of groundwaters level change, constructed from multiannual regime observations and from results of modeling
Integrated graphs of groundwaters level change, constructed from results modeling and from regime observation during August 2009 – September 2010
|
 |
|
 |
|||||||||
Previous |
Next |