
|
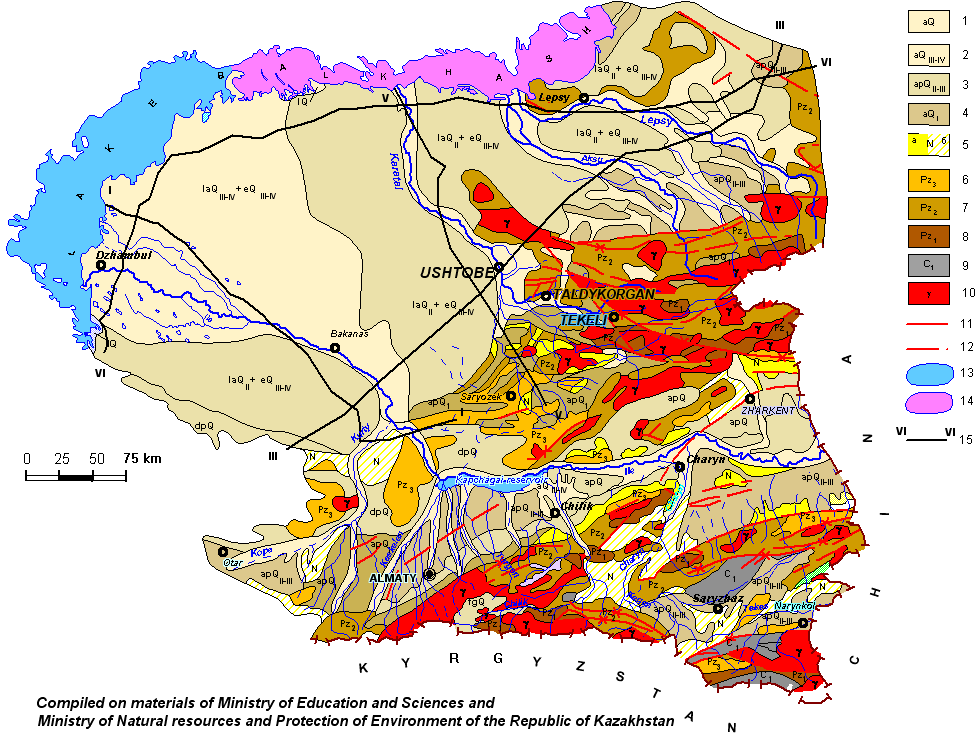
| Schematic hydrogeological map of Southern Pribalkhashye |
| Aquifers and aquiferous complexes: 1 - aquifers and aquiferous complexes of Quaternary alluvial, lacustrine (lQ) lacustrine-alluvial (laQ), alluvial-proluvial (apQ), deluvial-proluvial (dpQ) and fluvial-glacial (fgQ), depositions. Rubbly- coarse gravel formations, sands; 2 - aquifer of Upper-Quaternary-modern alluvial, alluvial-proluvial (apQIII-IV), lacustrine-alluvial (laQIII-IV), eolic (eQIII-IV) depositions. Sands; 3 - aquifers and aquiferous complexes of Middle-Upper-Quaternary alluvial-proluvial depositions. Coarse gravel, rubbly-coarse-gravel formations, inequigranular sands, 4 - aquifers and aquiferous complexes of Lower-Quaternary alluvial, alluvial-proluvial (apQI) and fluvial-glacial (fglQI) depositions. Sands, gravel-coarse gravel; 5 - a) aquifer of Neogenic depositions. Inequigranular sands, coarse gravel, weak sandstones; b) groundwaters of sporaradic distribution at the same depositions. Interlayers of sands and coarse gravels; 6 groundwaters of the zone of open jointing of Upper-Paleozoic rocks. Sandstones, conglomerates, effusive rocks and their tufas; 7 - groundwaters of the zone of open jointing of Middle-Paleozoic rocks. Limestones, aleurolites, gravelites, sandstones, schists, jaspers, diabase, porphirites, tufas; 8 - groundwaters of the zone of open jointing of Lower-Paleozoic rocks. Limestones, aleurolites, diabases, porphirites, tufas, sandstones, conglomerates, jasper, schists, quartzites; 9 - aquiferous of Lower-Carbon depositions. Limestones, dolomites; 10 - groundwaters of zone of open jointing of intrusive rocks. Granites, granodiorites, gabbro. 11 - aquiferous fissure, 12 - fissure, hydrogeological meaning of which is not clear; 13 - fresh water lake; 14 - salted lake; 15 - line of hydrogeological section |
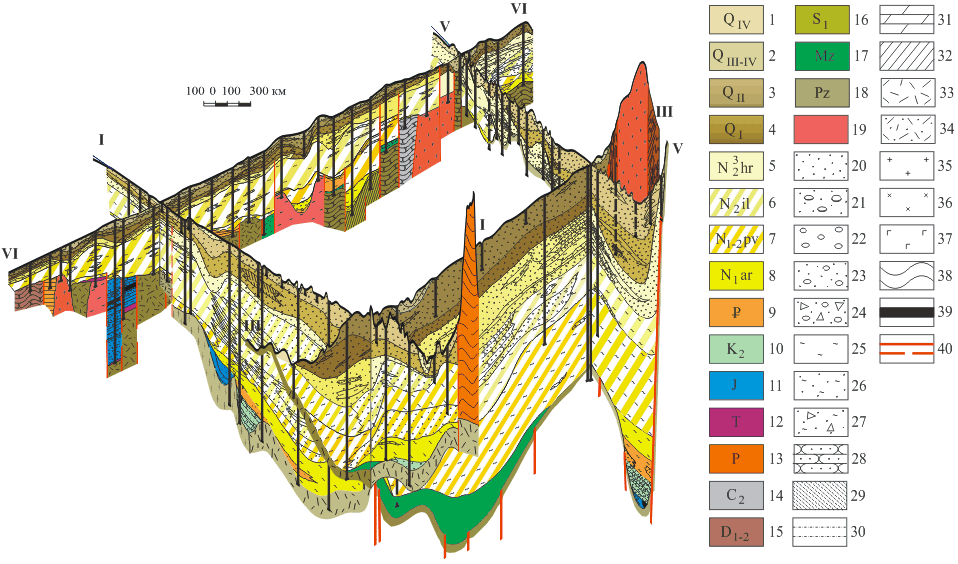 |
Three-dimensional diagram of Ili-Balkhash artesian basin lithological structure
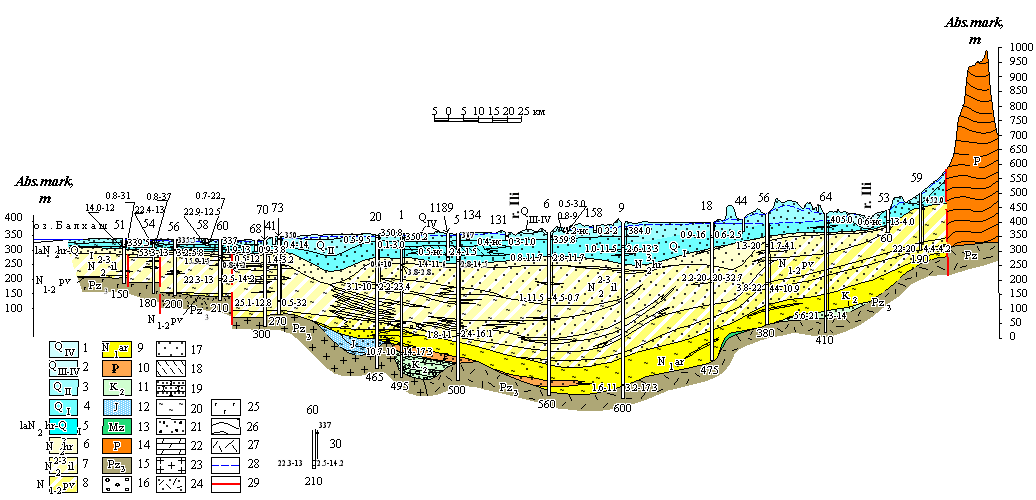 |
| Hydrogeological section by the line I-I |
| 1 aquifer of the modern depositions; 2 aquifer of the modern-Upper-Quaternary depositions; 3 aquifer of the Middle-Quaternary depositions; 4 aquifer of the Lower-Quaternary depositions; 5 aquiferous complex of the Lower-Quaternary and Upper-Pliocenic depositions;; 6 aquifer of the Chorgos suite depositions; 7 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Middle-Upper-Pliocenic depositions of Ili suite; 8 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Upper-Miocenic-Lower-Pliocenic depositions of Pavlodar suite; 9 aquicludeous depositions of the Aral suite; 10 aquifer of Oligocenic depositions; 11 aquifer of Upper-Carbonaceous depositions; 12 aquifer of Jurassic depositions; 13 aquicludeous depositions of Mezozoic crust of weathering; 14 groundwaters of jointing zone of Permian depositions; 15 groundwaters of jointing zone of Upper-Paleozoic rocks. Lithological composition of rocks: 16 gravel-pebbly depositions; 17 sands; 18 sandy loams; 19 sandstones; 20 clays; 21 gravel-pebble with sand filling ; 22 marls; 23 granites; 24 tuffs of acidic compositions; 25 grano-diorites; 26 tuffs of andesite and basalt porphyrites; 27 tuffs of basic composition.; 28 groundwaters level with free surface; 29 tectonic dislocation zone. 30 well. Numerals: above - number in catalogue; below depth, m. Arrow corresponds to head of groundwaters; near arrow - steady-state water level, m; from right: the first debit. l/s, the second depression, m; from left: the first water mineralization, g/l; the second water temperature, °Ρ |
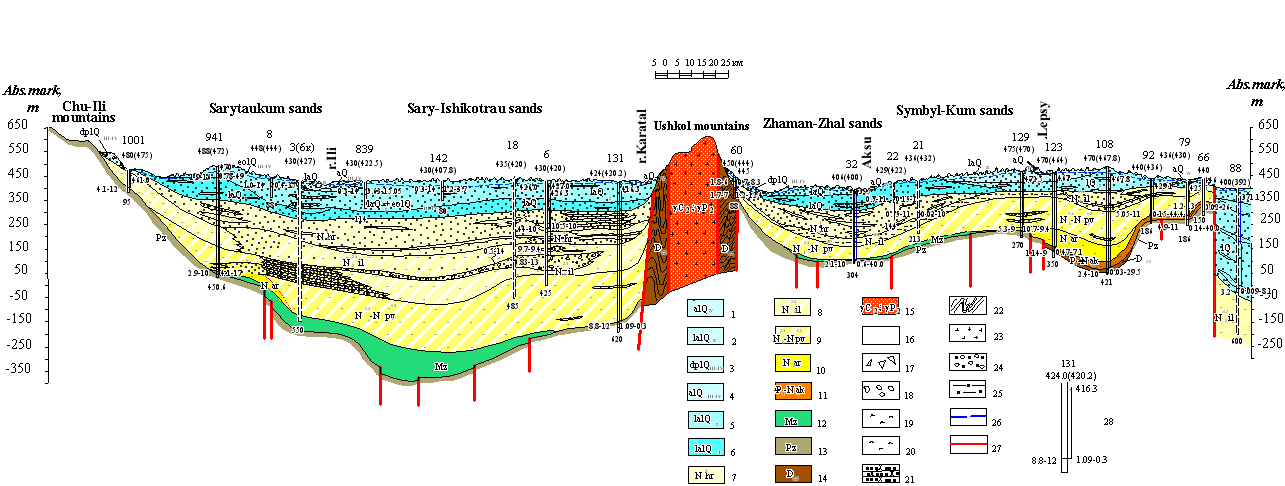 |
| Hydrogeological section by the line III-III |
| 1 aquifer of the modern lake-alluvial depositions; 2 aquifer of the Upper-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 3 aquifer of the modern-Upper-Quaternary deluvial-proluvial depositions; 4 aquifer of the modern-Upper-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions ; 5 aquifer of the Middle-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 6 aquifer of the Lower-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 7 aquifer of the Chorgos suite depositions; 8 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Middle-Upper-Pliocenic depositions of Ili suite; 9 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Miocenic depositions of Pavlodar suite; 10 aquicludeous depositions of the Aral suite; 11 groundwaters of sporadic distribution of Alakul suite depositions; 12 aquicludeous depositions of Mezozoic crust of weathering; 13 Paleozoic depositions. ; 14 aquicludeous Devonian depositions; 15 groundwaters of the zone of open jointing of intrusive Middle-Carboniferous, Upper- Permian rocks; 16 sands; 17 rock-debris-pebbly depositions with sand filling; 18 boulder-pebbly depositions with sand-filling; 19 sandystone clays; 20 clays; 21 sandstones; 22 sedimentation-effusive rocks;; 23 granites; 24 gravel-pebbly depositions with sand filling; 25 aleurolites. ; 26 groundwaters level with free surface; 27 supposed tectonic dislocations zone; 28 well. Numerals above number in catalogue, lower absolute mark of wellhead, in brackets absolute mark of water table. Arrow corresponds to head of groundwaters. Numeral near arrow absolute mark of piezometric level of water. Numerals from right: first debit, l/s; the second depression, m. Numerals from left: the first water mineralization, g/l; the second water temperature, °Ρ. Numerals at the bottom well depth, m |
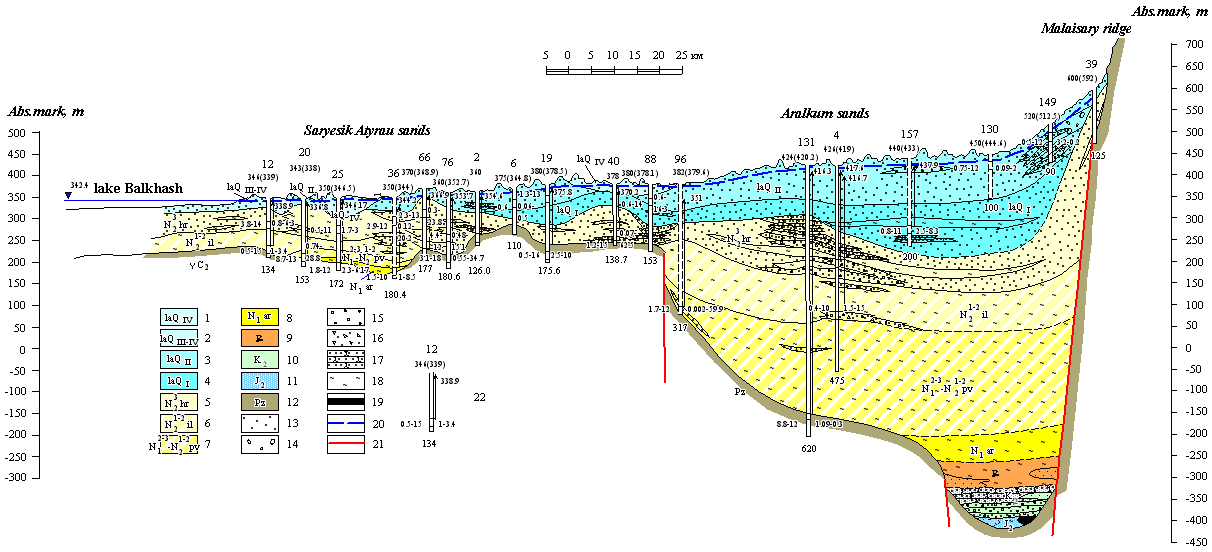 |
| Hydrogeological section by the line V-V |
| 1 aquifer of the modern lake-alluvial depositions; 2 aquifer of the modern -Upper-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 3 aquifer of the Middle-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 4 aquifer of the Lower-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 5 aquifer of the Chorgos suite depositions; 6 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in depositions of Ili suite; 7 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Miocenic-Pliocenic depositions of Pavlodar suite; 8 aquicludeous depositions of the Aral suite; 9 aquifer of Paleogenic depositions; 10 aquifer of Upper-Carbonaceous depositions; 11 aquifer of Upper-Jurassic depositions; 12 Paleozoic depositions. Lithological composition of rocks: 13 sands; 14 gravel-pebbles; 15 pebbles; 16 Rock-debris with sand; 17 sandstones; 18 clays; 19 coals. 20 groundwaters level with free surface; 21 tectonic dislocations zone; 22 well. Numerals above number in catalogue, lower absolute mark of wellhead, in brackets absolute mark of water table. Arrow corresponds to head of groundwaters. Numeral near arrow absolute mark of piezometric level of water. Numerals from right: first debit, l/s; the second depression, m. Numerals from left: the first water mineralization, g/l; the second water temperature, °Ρ. Numerals at the bottom well depth, m |
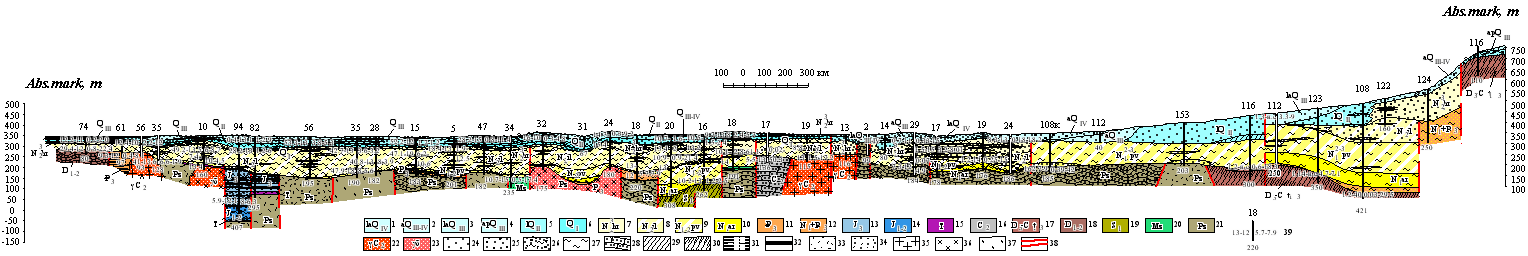 |
| Hydrogeological section by the line VI-VI |
| 1 aquifer of the modern lake-alluvial depositions; 2 aquifer of the modern -Upper-Quaternary alluvial depositions; 3 aquifer of the Upper-Quaternary lake-alluvial depositions; 4 aquifer of the Upper-Quaternary alluvial-proluvial depositions; 5 aquifer of the Middle-Quaternary lake depositions; 6 aquifer of the Lower-Quaternary depositions; 7 aquifer of the Chorgos suite depositions; 8 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Middle-Upper-Pliocenic depositions of Ili suite; 9 groundwaters of sporadic distribution in Upper-Miocenic-Lower-Pliocenic depositions of Pavlodar suite; 10 aquicludeous depositions of the Aral suite; 11 aquifer of Oligocenic depositions; 12 groundwaters of Lower-Pliocenic-Oligocenic depositions; 13 aquifer of Upper-Jurassic depositions; 14 aquifer of Lower-Middle-Jurassic depositions; 15 groundwaters of Triassic depositions; 16 aquiferous zones of jointing in Middle-Carboniferous depositions; 17 groundwaters of Upper-Devonian and Tournaisian rocks; 18 groundwaters in Lower and Middle Devonian depositions; 19 aquiferous zones of jointing of Lower-Silurian rocks; 20 aquicludeous depositions of Mezozoic crust of weathering; 21 groundwaters of open jointing zone of non-segmented Paleozoic rocks; 22 groundwaters of open jointing zone of intrusive Middle-Carboniferous rocks; 23 groundwaters of jointing zone of rocks of Paleozoic intrusive complex. Lithological composition of rocks: 24 sands; 25 gravel-pebbly depositions with sand filling; 26 rock-debris-clayish depositions; 27 clays; 28 sandstones; 29 sandy loams; 30 schists; 31 aleurolites; 32 coals; 33 tuffs; 34 tuffs of acidic compositions and tuff-sandstones; 35 granites; 36 diorites; 37 tuffs of mean structure. 38 tectonic dislocations zone. 39 well. Numerals: above number in catalogue; below depth, m; from right: the first debit, l/s, the second depression, m; from left: the first water mineralization, g/l; the second water temperature, °Ρ |
Waters of Paleozoic rocks. Paleozoic formations occur, on the territory described, from 25-100 m near the side of parts and to 400-1000 m at the zone of the maximal trough. Paleozoic basement is represented basically by effusive-sedimentary complex of rocks diabase porphyrites, aleurolites, argilites, sandstones, which in some places are ruptured by granite intrusions. Waters of Paleozoic depositions are tapped on the depths from 50-100 m in western part of the depression up to 400-600 m in eastern one. Waters are highly pressurized, sometimes auto-discharging. Their mineralization changes from 2 to 10 g/l.
Waters of Paleogenic depositions. Paleogenic depositions are represented by clays with aquiferous interlayers and lenses of sandstones. They are spread only in southern and eastern part of the territory described. Depth of their bedding is 600-800 m. Waters are highly pressurized, sometimes auto-discharging. Mineralization is 3-5 g/l.
Waters of Neogenic depositions. Neogenic complex of depositions is represented predominantly by clays of Aralski, Pavlodarski and Ileiski suites [Dzhabasov M.Kh., Karagodin P.F., Oshlakov G.G., Geological-Hydrogeological conditions of Southern-Pribalkhashski depression in the light of the new data / In the book: Regional hydrogeological investigations in Kazakhstan. Alma-Ata: Nauka, 1971. pp. 51-57 (in Russian)]. They contain, especially in Ileiski suite, lenses of water-bearing rudaceous rocks. The greatest amount of lenses is contained near the sides of the depression. Groundwater are isolated in depositions of Pavlodarski and Ileiski suites of Neogene.
Waters of Pavlodarski suite of Neogene are contained in separate lenses of sand and sandstone, and in piedmont zone in gritstones and gravels-coarse gravels with sandy filler. Thickness of depositions near 300 m in the central part of the depression and that of water-bearing rocks 5-27 m. Waters are pressurized, value of the head is more than 100 m. Water-bearings rocks roofing bedding thickness changes from 20 to 142 m. Wells debits 1,9-5,7 l/sec with level decrease of 5-20 m. Mineralization changes from 1-3 g/l in southern and south-eastern parts up to 3-15 g/l with departure from mountains to the lower course of the river Karatal. Chemical composition changes from sodium sulphate up to sodium sulphate-chloride.
Waters of Ileiski suite of Neogene are contained in sands occurring in the form of lenses among pale yellow, greenish-gray clays. Rocks thickness changes from some metres up to 100-150 m, sometimes up to 180 m. Water-bearing lenses thickness measures 5-20 m, reaching in separate cases 45-60 m. Water-bearing depositions tapping depth changes from 65 to 160-360 m. Groundwaters are pressurized. Head value measures 100-177 m. Wells debits oscillate from 0,67 to 3,4 l/sec under level decrease for 3-42 m. Groundwaters mineralization changes from 0,5-2 to 3-10 g/l.
Waters of Khorgos suite of Neogene and Lower-Quaternary depositions. These depositions are widely distributed in Southern-Pribalkhashski depression. Upper- and Middle-Quaternary depositions serve as the roof, and sedimentations of Ileiski suite of Neogene serve as the bottom. They are represented by small and fine- grained sands with inter- layers and lenses of sandy loams and clays, more seldom by sandstones gravels coarse gravels. Unification of Lower-Quaternary and Khorgos formations into one aquifer is dictated by absence of aquiferdeous depositions between them. Water-bearing depositions thickness oscillates from 16-44 m on the north up to 65-135 m on the south. Groundwaters in depositions have close hydraulic connection with waters of Upper- and Middle-Quaternary depositions. Aquifers in Upper-, Middle-, Lower-Quaternary and Khorgos depositions are one water-bearing rock mass with free surface of groundwaters level. Groundwaters bedding depth is 38-130 m. In central part of the depression waters are pressurized. Here piezometric levels are set up on the depths of 2,7-8 m. On the remaining part of the depression waters have ground character and are situated on the depths up to 50 m. Boreholes debits change from 0,02-3 to 5-12 l/sec under lowered level 5-15 m. Water mineralization docs not surpass 1-3 g/l, as of the chemical character, they are hydrocarbonate calcium, seldem sulphate, chloride sodium.
Waters Middle-Upper-Quaternary alluvial- proluvial depositions. They are distributed on the east of Southern-Pribalkhashye depression. Total thickness of depositions 250-300 m. As of lithological composition there are alternating aquiferous and aquifard rocks, represented by boulder- and gravel-coarse gravels with sandy filler, clays, loams, more seldom, sandy loams. Aquiferous depositions thickness 60-100 m, and aquifard ones from 1-3 to 10-15 m. Predominantly waters are highly-pressurized. Mineralization changes from 0,2 to 8 g/l, as of the chemical composition these are mainly hydrocarbonate calcium, more seldom hydrocarbonate- sulphate sodium ones.
Waters of Middle-Upper-Quaternary lacustrine-alluvial and overlapping them modern depositions are most widely developed in the depression, where they form thick flow of groundwaters, moving from south to north, to the side of lake Balkhash. Basic water-bearing rocks in sandy massives are predominantly sands, in some places they contain interlayers of clays, loams and sandy loams. Aquifers thickness reaches 200-240 m in the central part of the depression, decreasing to 50-70 m near Balkhash lake. Groundwaters bedding depth in interhummocky and interridge depressions in eastern part of sands does not surpass 5 m and on hummocks and ridges it reaches 10-15 m. In the modern rivers valleys and on Balkhash shore they are tapped on the depth to 5 m. On the right shore of the river Karatal waters are dipping to the depth of 30-80 m in depressions and to 100-130 m on ridges and hummocks. Boreholes debits change from 0,1-0,5 to 2-5 l/sec, sometimes boreholes productivity reaches 10-30 l/sec with lowering of water level on 5-20 m. Groundwaters mineralization is predominantly equal to 1-3 g/l, on the parts of separating ridges and near lake Balkhash their mineralization increases to 3-10, in some places to 50 g/l. As of chemical composition these are hydrocarbonate calcium, sodium and sulphate sodium ones, with increate of mineralization, water composition changes from sulphate- chloride sodium to chloride sodium.
Waters of Upper-Quaternary-modern depositions are conected with alluvial formations of the valleys of the rivers Ile and Karatal. As water-bearing rocks here serve small- and finegrained dusty sands, and in piedmont regions alluvial-proluvial gravels-coarse gravels. Groundwaters bedding depth is 1-5 m, sometimes they are drawing nearer to the day surface, forming small lakes, sors, solonchaks. Boreholes debits change, in accordance with lithological composition of water-bearing depositions, from 5-15 l/sec with lowering of water level to 3-5 m in piedmont regions to 0,5-1 l/sec with lowering water level to 2-5 m with departure from rivers. Waters are predominantly fresh, mineralization of them is 0,5-1 g/l, as of the chemical composition they are hydrocarbonate calcium, sodium.
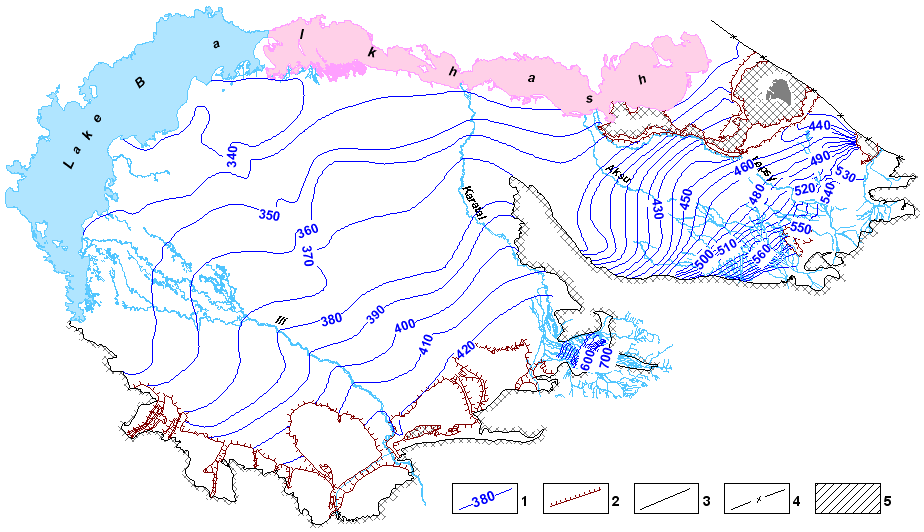 |
Map of hydroisohypses of aquiferous complex of Quaternary depositions of Ili-Balkhash and Alakol basin of groundwaters
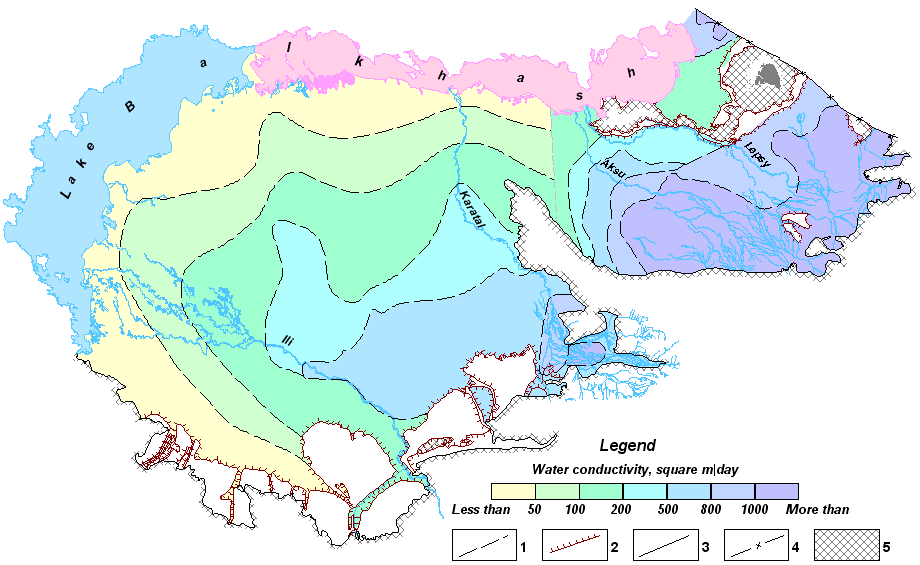 |
Map of conductivity of aquiferous complex of Quaternary depositions of Ili-Balkhash and Alakol basin of groundwaters
 |
|
 |
|||||||||
Previous |
Next |